In a world first, Suntory Global Innovation Center Limited identified a novel compound present in green coffea arabica beans; an isomer of 3-Methylbutanoyl Glycosides. It was revealed that high quality beans contain high concentrations of this compound as well as another isomer of 3-Methylbutanoyl Glycosides, and that these compounds enhance the flavor and aroma of the coffee after the roasting and brewing process. This research was jointly led by Professor Hiroyuki Wariishi of the Innovation Center for Medical Redox Navigation, Kyushu University, and Doctor Chifumi Nagai of the Hawaii Agriculture Research Center (HARC), and it was presented in the Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry*1 (April 2, 2015).
▼ Presentation Title
Identification of 3-Methylbutanoyl Glycosides in Green Coffea arabica Beans as Causative Determinants for the Quality of Coffee Flavors.
▼Presenters
IWASA Keiko*, SETOYAMA Daiki**, SETA Harumichi*, SHIMIZU Hiroaki*, FUJIMURA Yoshinori**, MIURA Daisuke**, WARIISHI Hiroyuki**, NAGAI Chifumi***, NAKAHARA Koichi*.
| |
*Suntory Global Innovation Center Co. Ltd, Osaka, JP. ** Innovation Center for Medical Redox Navigation, Kyushu University, Fukuoka, JP. *** Hawaii Agriculture Research Center (HARC), Hawaii, USA. |
< Background >
The flavor and aroma of coffee beverages are influenced by roasting and brewing process, however, the most significant determinant is the quality of the coffee beans themselves. Suntory Global Innovation Center Limited engages in research that objectively and scientifically evaluates the quality of pre-roasted coffee beans. In this study, we used metabolomics*2 technology to analyze the chemical compounds contained in green coffee beans (metabolites) and their impact upon the flavor of the resultant coffee beverage.
| *2 |
Metabolomics refers to the comprehensive and objective analysis of metabolites. Metabolites are chemical compounds produced by the biological activity of plants, animal, and microorganism cells. Metabolomics analyzes a various samples of such chemical compounds to determine differences in properties. |
<Test A>
| (1) |
Thirty-six samples of green coffee beans were procured from various producers and locations, and crushed into powder. The powder was extracted with 70% methanol/H2O, and subjected to LC-MS measurements*3. A total of 2,649 signals of metabolomic information (valid peaks) were obtained.
The same samples of beans were roasted and then organoleptically evaluated by an experienced Licensed Q grader*4 in accordance with SCAA*5 protocol. Each sample of beans was awarded a grade. |
| (2) |
Multivariate statistical analysis*6 was used to analyze the relationship between the metabolomic information in green beans measured by LC-MS and the SCAA cupping score for the resultant beverage. The compounds present in high-scoring beans were then explored. |
| (3) |
NMR spectroscopy*7 and high resolution MS*8 were performed to determine the chemical structure of two key compounds explored in (2). |
| |
*3 |
Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry is a method for qualitatively and quantitatively analyzing a sample of compounds. It involves separating the compounds based on their different degrees of compatibility with the stationary phase and the mobile phase, and then detecting the separated compounds using a mass spectrometer. |
| *4 |
A coffee sensory evaluator licensed by the Coffee Quality Institute (CQI). |
| *5 |
SCAA is an abbreviation of the Specialty Coffee Association of America. SCAA determines the protocols for cupping, an internationally recognized method for definitive coffee evaluation. |
| *6 |
Multivariate statistical analysis is a statistical method that uses a large amount of data (variables) to clarify correlation between multiple variables. |
| *7 |
NMR spectroscopy is an abbreviation of Nuclear Magnetic Resonance spectroscopy. It is an analytical technique that determine the chemical structures of compounds by exploiting the phenomenon of nuclear magnetic resonance, in which nuclei in a magnetic field resonate when the energy of the field is at the specific resonance frequency of the atoms. |
| *8 |
Mass resolution is used to measure the ability to distinguish two MS signals of slightly different m/z in a mass spectrum, thereby providing criteria for quantitative analysis. High-performance MS enables the calculation of the compositional formula of compounds. |
<Results A>
| (1) |
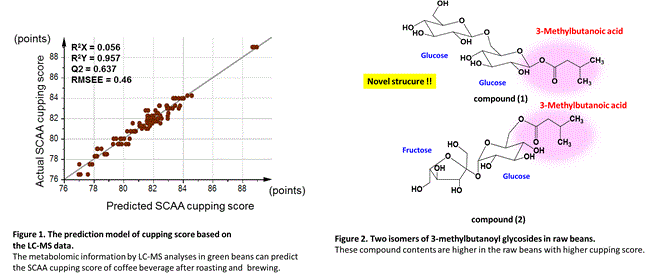
With regard to Test A-(1)&(2), there was a strong correlation between the metabolomic information in green beans and the SCAA cupping score, revealing that metabolomic information is a precise predictor of SCAA cupping score (see Figure 1). |
| (2) |
With regard to Test A-(3), the two key compounds explored in Test A-(2) were revealed to be two isomers of 3-Methylbutanoyl Glycosides*9, and their chemical structures were clarified (see Figure 2). The second compound is a known compound in coffee beans*10, but the first compound has a novel structure consisting of two glucose and a naturally occurring compound called 3-methylbutanoic acid (the scientific name of this compound is 6’-O-(β-D-glucopyranosyl)-1’-O-[3-methylbutanoyl]-β-D- glucopyranose). Suntory Global Innovation Center Limited is thus the first in the world to discover this novel compound. |
| *9 |
Both compounds were composed of the same elements in the same proportions, but different structures. The two compounds differ in terms of positions at which the 3-methylbutanoic acid and the glucose join, as well as the type of glucose (see Figure 2). |
| *10 |
Reference 1: Weckerle, B. et.al. Phytochemistry. 2002, 60, 409-414.
Compound Name: 3-Methylbutanoyl-6-O-α-D-glucopyranosyl-β-D-fructofuranoside |
<Test B>
| (1) |
The two isomers of 3-Methylbutanoyl Glycosides explored in Test A-(2) were subjected to pyrolysis under the model conditions of roasting (230 °C, 10 minutes), and the products were analyzed using GC-MS*11. |
| (2) |
The pyrolysis products of the two isomers of 3-Methylbutanoyl Glycosides were added to coffee brew at a concentration of 100 ppb. The coffee was then submitted to a sensory evaluation by a Licensed Q Grader in order to assess the impact of the additive upon flavor. |
| *11 |
GC-MS is an abbreviation of Gas Chromatogram-Mass Spectrometry. Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry is a method for qualitatively and quantitatively analyzing a sample of compounds. It involves vaporizing the compounds and separating them using a chromatogram, and then detecting the separating compounds using a mass spectrometer. |
<Results B>
| (1) |
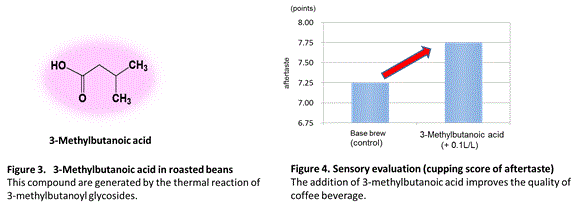
The pyrolysis products of both isomers of 3-Methylbutanoyl Glycosides were identified to be the 3-methylbutanoic acid (see Figure 3). |
| (2) |
Adding 3-methylbutanoic acid to the coffee brew significantly improved aftertaste score*12, confirming that the additive clearly improves the flavor of the coffee beverage (see Figure 4). It was concluded that the presence of very small quantities of 3-methylbutanoic acid in coffee liquid improves the flavor of the coffee. |
| *12 |
Aftertaste is a significant factor for coffee flavor. It is defined as the length of the positive flavor qualities emanating from the back of the palate and remaining after the coffee is expectorated or swallowed. If the aftertaste were long and pleasant, a higher score would be given. |
<Future Prospects>
In this study, we revealed that metabolomic information in green beans can predict the quality of the resultant beverage, and we identified two isomers of 3-Methylbutanoyl Glycosides which are correlated with high cupping score.
Using 3-Methylbutanoyl Glycosides as a marker should aid the development of technologies for objectively assessing the quality of green beans and distinguishing high quality green beans, as well as manufacturing technologies for improving the quality of coffee beverages.
Suntory Beverage & Food Limited Group Companies will continue collaboration with Suntory Global Innovation Center with a view to utilizing these research results for the creation of added value in the beverage and food manufacture and retail sector.
Suntory Global Innovation Center Limited website : https://www.suntory.com/sic/
Suntory Beverage & Food Limited website : https://www.suntory.com/sbf/
|



